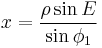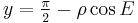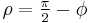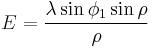Bottomley projection
A Bottomley projection is an equal-area map projection.
The projection is:
where
and φ is the latitude, λ is the longitude from the central meridian, and φ1 is the given parallel of the projection which determines its shape, all in radians.
Parallels (i.e. lines of latitude) are concentric elliptical arcs of constant eccentricity, centred on the north pole. On the central meridian, shapes are not distorted, but elsewhere they are. Different projections can be produced by altering the eccentricity of the arcs, making it vary between the sinusoidal projection and the Werner projection.
It was introduced by Henry Bottomley as an alternative to the Bonne projection to reduce the extent of extreme distortion at the edges and give a more satisfying overall shape.